What are zoonotic diseases and how dangerous are they?
One Health Graphics One Health CDC

Zoonoses are the "diseases and infections that are naturally transmitted between vertebrate animals and man," as defined in 1951 by the World Health Organization (WHO) Expert Committee on Zoonoses. The word zoonosis (plural zoonoses) is the combination of two Greek words ( zoon, animals and noson, disease), and was coined at the end of the.
Frontiers Emerging and reemerging zoonotic viral diseases in Southeast Asia One Health challenge

Abstract. Zoonoses represent a public health risk recently pointed out by the spreading of previously unknown human infectious diseases emerging from animal reservoirs such as severe acute respiratory syndrome and avian influenza caused by H5N1 -virus. These outbreaks have shown that animal breeding activities can pose a significant public.
ROLE OF VETS IN ONE HEALTH APPROACH TO TACKLE THE EMERGING ZOONOSES LIKE COVID19 Pashudhan

The Tripartite Zoonoses Guide (TZG) has been jointly developed by the FAO, WHO, and WOAH to support countries in taking a multisectoral, One Health approach to address zoonotic diseases. It provides principles, best practices and options to assist countries in achieving sustainable and functional collaboration at the human-animal-environment.
One Health Approach for the Control of Zoonotic Diseases ScienceOpen

Zoonotic diseases have a significant impact on both human and animal health globally. The present study was planned to prioritize the zoonoses in Punjab state of India. To develop a zoonotic disease prioritization scoring system, a comprehensive approach has been taken, including literature review, key person interviews with animal health experts (n = 12) and medical professionals (n = 7), and.
World Zoonosis Day 6 July Online learning supports governments to operationalize a One Health

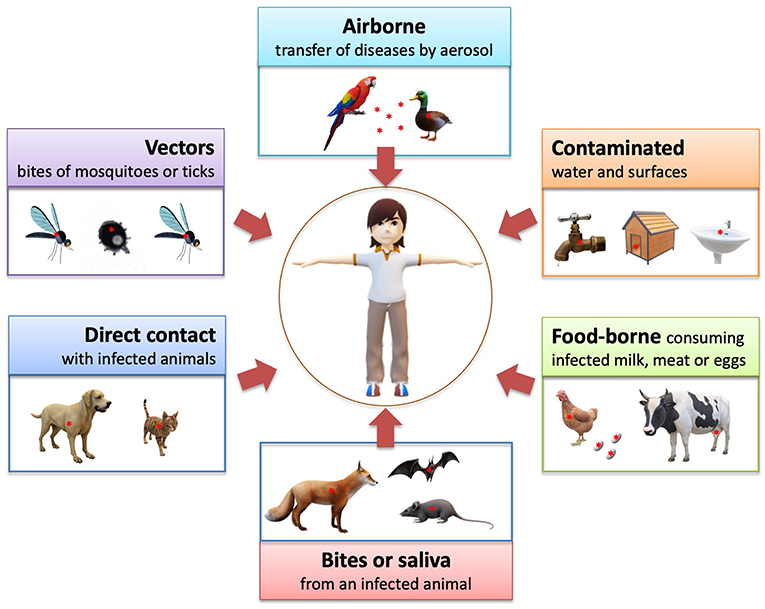
Introduction. According to the Joint WHO/FAO Expert Committee on Zoonoses, Second Report, in the year 1959, zoonoses (the expression zoonotic diseases is also used) are "those diseases and infections which are naturally transmitted between vertebrate animals and man.". The transmission may take place directly or indirectly by means of vectors.
One Health, Many Approaches CDC Fosters a One Health Strategy in NPHIs Division of Global
The one health approach continues to be a highly investigated concept, via the pursuit of scholarly resources involving the health of humans, animals, and the environment. There is a need to increase research on zoonoses, food safety, and agriculture and to improve the understanding of the one health concept.
Strengthening a One Health Approach to Emerging Zoonoses The Royal Society of Canada

Recurring outbreaks of emerging and re-emerging zoonoses, such as Ebola virus disease, avian influenza, and Nipah virus, serve as a reminder that the health of humans, animals, and the environment are interconnected and that early response to emerging zoonotic pathogens requires a coordinated, interdisciplinary, cross-sectoral approach. As our world becomes increasingly connected, emerging.
Zoonoses HealthforAnimals
Immunological aspects of emerging and re-emerging zoonoses. Zoonoses, a group of diseases that are transmitted between animals and humans, are considered as the most prevalent infections in humans ( 1 ). They present substantial global health threats and continue to pose significant challenges to both the scientific community and public health.
One Health Approach for the Control of Zoonotic Diseases ScienceOpen

Zoonoses represent a public health risk recently pointed out by the spreading of previously unknown human infectious diseases emerging from animal reservoirs such as severe acute respiratory syndrome and avian influenza caused by H5N1-virus. These outbreaks have shown that animal breeding activities can pose a significant public health risk.
(PDF) One Health Approach for the Control of Zoonotic Diseases

Zoonoses represent a public health risk recently pointed out by the spreading of previously unknown human infectious diseases emerging from animal reservoirs such as severe acute respiratory syndrome and avian influenza caused by H5N1 -virus. These outbreaks have shown that animal breeding activities can pose a significant public health risk.
Zoonoses—Diseases Naturally Transmitted From Animals to Humans · Frontiers for Young Minds
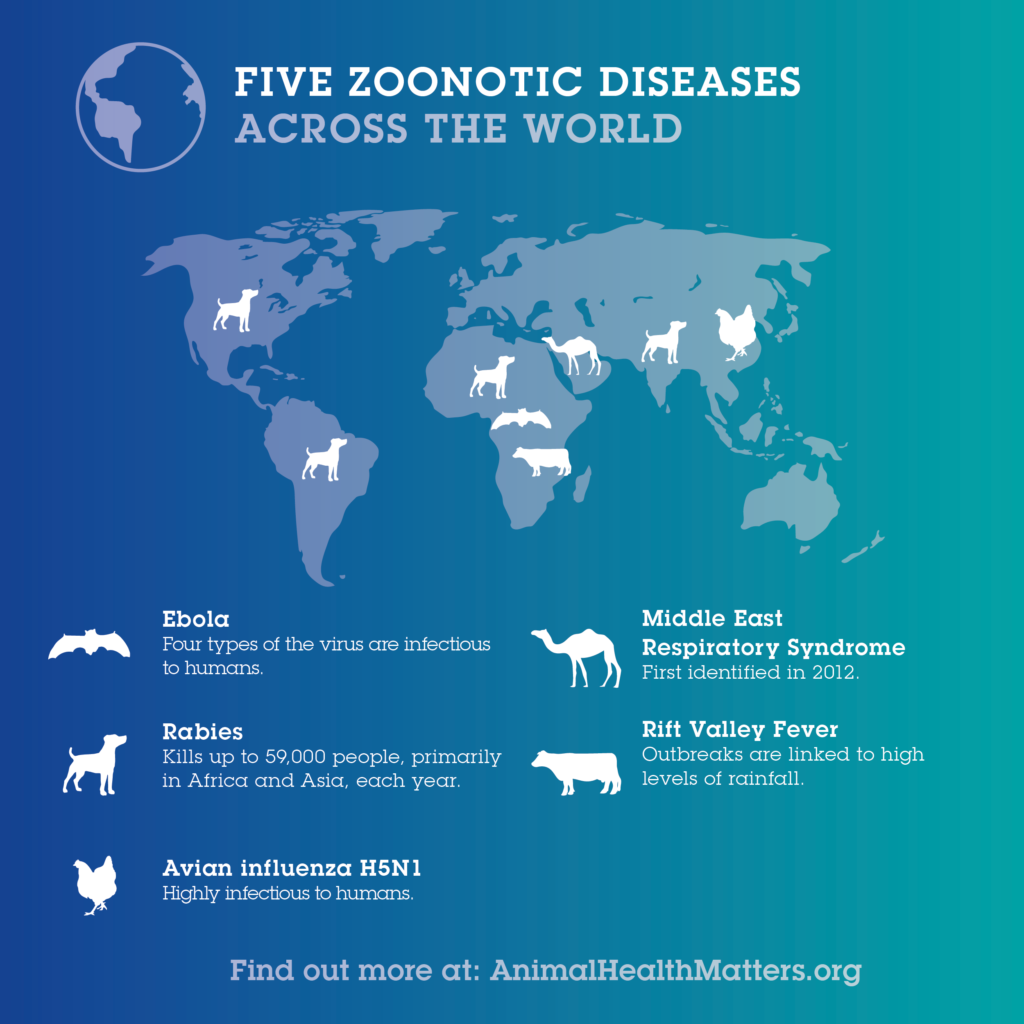
2. Classification of Zoonoses. Zoonotic diseases are caused by a wide range of pathogens. Based on etiology, zoonoses are classified into bacterial zoonoses (such as anthrax, salmonellosis, tuberculosis, Lyme disease, brucellosis, and plague), viral zoonoses (such as rabies, acquired immune deficiency syndrome- AIDS, Ebola, and avian influenza), parasitic zoonoses (such as trichinosis.
What are zoonotic diseases and how dangerous are they?
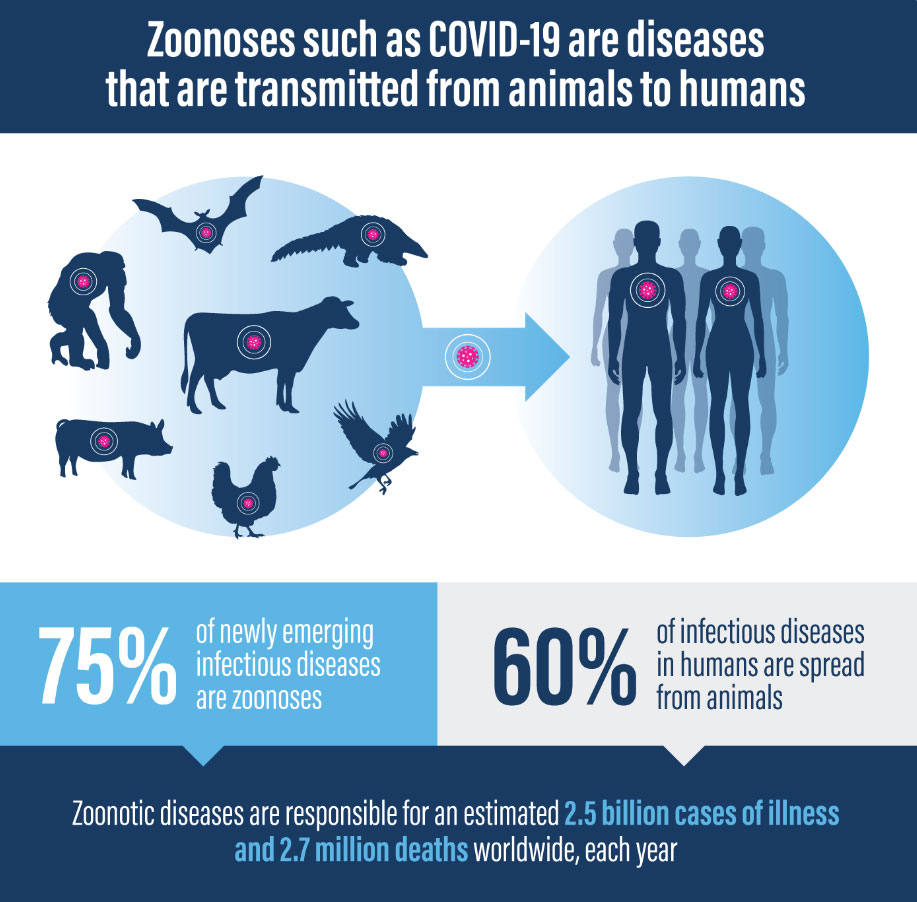
The human population has doubled in the last 50 years from about 3.7 billion to approximately 7.8 billion. With this rapid expansion, more people live in close contact with wildlife, livestock.
One Health Veterinary Schools Council UK

Current scenario in communicable diseases has generated new era that identifies the "One health" approach to understand the sharing and management of etiological agents with its impact on ecosystem. Under this context the relevance of zoonotic diseases generates major concern. The indiscriminate and higher use of antibiotics in animal husbandry creates substantial pressure on the gut.
Understanding Emerging Zoonotic Diseases on a Global Scale with Dr. Tracey Goldstein

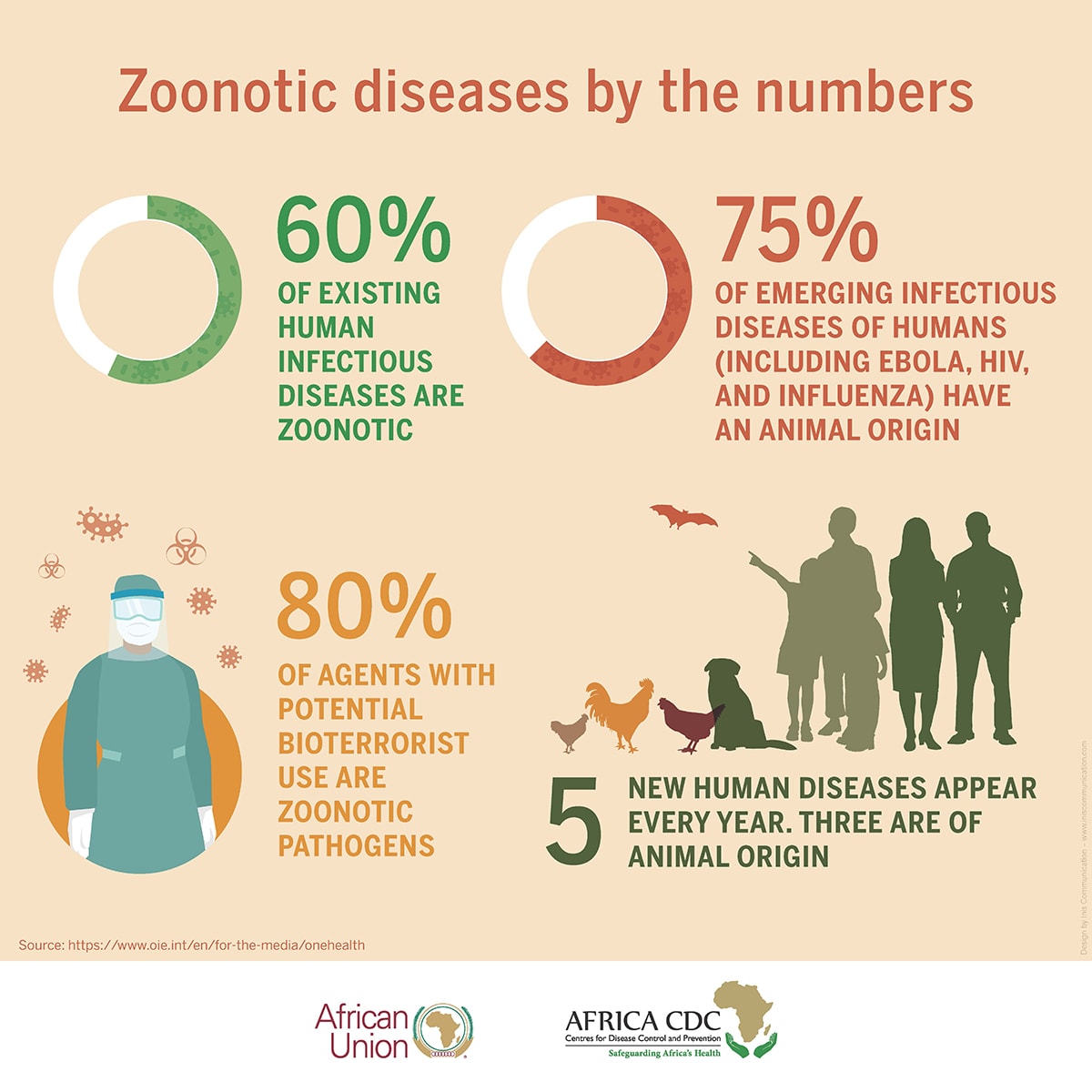
Zoonotic diseases are the infections that are transmitted between animals and humans and are a major source of emerging infectious diseases. Nearly >60% of the pathogens that infect humans cause zoonotic diseases in humans. The highest zoonotic disease burden, with widespread illness and death, is prevalent in Ethiopia, Nigeria, Tanzania, and.
Different types of zoonoses and factors affecting prevalence of... Download Scientific Diagram

Emerging Zoonoses and One Health Approach. September 2020. In book: Zoonoses: Recent Approaches to Contain the Global Zoonotic Burden (pp.50-54) Edition: 1. Publisher: Meat Technology Unit, KVASU.
Zoonosis and One Health Concep [IMAGE] EurekAlert! Science News Releases
The emergence and re-emergence of zoonotic diseases is not new, and over the past three decades the onset of outbreaks of infectious diseases emerging from animal reservoirs to infect humans has increased. For example, Ebola virus, highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) viruses, and the coronaviruses severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS.
.